Thurs., 10/13/11 Polytrauma, Paper #30, 3:25 pm OTA-2011
Does Pain Correlate With Patient-Based Functional Outcome Scores After Commonly Operatively Treated Fractures?
Clifford B. Jones, MD, FACS1; Debra L. Sietsema, PhD1; Gillian L. Sembler Soles, MD2;
Paul Tornetta, III, MD2;
1Orthopaedic Associates of Michigan, Michigan State University, Grand Rapids, Michigan, USA;
2Boston University Medical Center, Boston, Massachusetts, USA
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to evaluate the correlation of a validated visual analog scale (VAS) for pain with the Short Musculoskeletal Function Assessment (SMFA) indices in patients treated operatively for common fracture patterns: proximal humerus, distal radius, pelvic ring, acetabulum, and tibial plateau.
Methods: A consecutive cohort of 140 patients with proximal humeral fractures, 32 patients with unstable distal radius fractures, 205 patients with pelvic ring injuries, 67 patients with acetabular fractures, and 92 patients with tibial plateau fractures who were treated operatively and followed for >6 months comprise the study group. SMFA and VAS pain scores (10-point scale) were prospectively collected. The SMFA indices were correlated with the VAS, age, gender, and the SMFA question 46 (“How much are you bothered by problems with stiffness and pain?”).
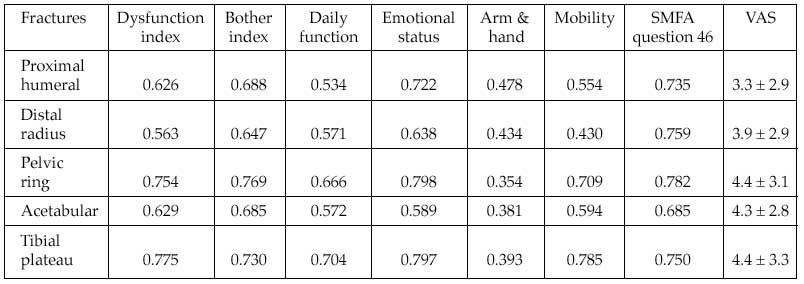
Results: The dysfunction and bother indices were recorded for the fractures respectively as follows: proximal humeral, 24.0 and 23.6; distal radius, 23.1 and 28.3; pelvic ring, 27.2 and 30.8; acetabular, 27.8 and 28.3; and tibial plateau, 28.0 and 28.0. Age did not relate to pain for proximal humeral, distal radius, or acetabular fractures (P >0.05). However, pain inversely related to age in patients who had pelvic ring and tibial plateau fractures (P <0.001). No difference was present between males and females regarding pain for any of the studied fractures. Significant correlations were found between pain and all SMFA indices and the SMFA question 46 for all studied fractures (P <0.01).
Correlation of SMFA With VAS, Pearson Correlation Coefficient (r): P <0.01 for All

Conclusions: Our findings suggest that pain, measured by a validated VAS scale, is an important factor in the explanation of SMFA results for patients with common operatively treated traumatic fractures. Knowing whether pain relates to musculoskeletal outcome can affect interventions related to pain management, rehabilitation, and return to previous activities. Pain should be investigated further concerning clinical outcomes and function measurements.
Alphabetical Disclosure Listing (628K PDF)
• The FDA has not cleared this drug and/or medical device for the use described in this presentation (i.e., the drug or medical device is being discussed for an “off label” use). ◆FDA information not available at time of printing. Δ OTA Grant.