OTA 2008 Posters
Scientific Poster #129 Upper Extremity OTA-2008
Prospective Randomized Controlled Orthopaedic Surgery for Colles-Type Radius Fractures: K-Wires versus Multidirectional Fixed-Angle Plate
Christian Probst, MD1 (a-Grant by H & S Re Insurance Company, Grant from Medartis,
Basel, Switzerland); Reinhard Meier, MD2 (a-Grant from Medartis, Basel, Switzerland);
Ralf Gaulke, MD1 (n); Christian Krettek, MD1 (a-AO Foundation);
1Hannover Medical School, Department of Trauma, Hannover, Germany;
2Würzburg University Hospital, Department of Trauma, Würzburg, Germany
Hypothesis: Colles-type distal radius fractures are among the most common fractures in humans. Despite frequent surgical treatment, there is a lively discussion on the proper surgical strategy and implant. We examined the results of minimal invasive closed reduction and Kirschner wire (K-wire) fixation with palmar open reduction and multidirectional fixed-angle plate osteosynthesis (Aptus System, Medartis).
Methods: We included 103 consecutive patients between 2003 and 2004 in our prospective randomized controlled trial. Inclusion criteria were new (<72 h) Colles-type distal radius fracture and age 18 to 80 years. Exclusion criteria were prevalent lesion of the fractured wrist, systemic diseases such as diabetes or carcinoma, and pregnancy. Patients were randomized in the emergency department after informed consent was obtained. Standardized follow-up included clinical examination, Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder and Hand (DASH) score, range of motion (neutral-null method), grip strength (Jamar dynamometer), and radiographs at 12 months after trauma. Significance was set at P <0.05
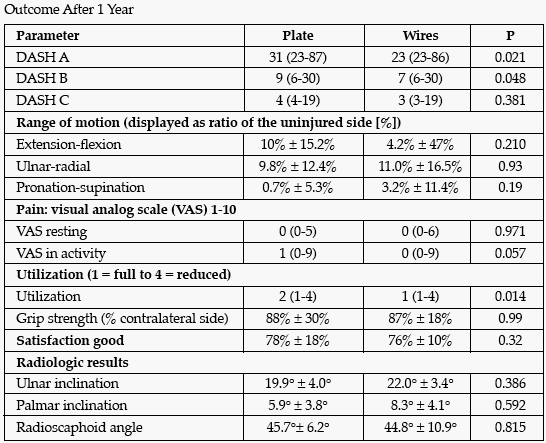
Results: 94 patients (plate, n = 50; wires, n = 43) finished the study. The 1-year outcome is shown in the table below. Complications were seen in 8 patients (plate, 3; wire, 5).
Conclusion: Patients after closed reduction and K-wire osteosynthesis plus cast or external fixator showed a functional advantage over the plate group. If detailed type of fracture and expectations of patients remain unconsidered, morbidity associated with the operative approach or implants remaining in situ seem to affect patient outcome.
Significance: Closed reduction and K-wire fixation of distal radius fractures of Colles type may be superior to open reduction and multidirectional fixed-angle plate osteosynthesis.

If noted, the author indicates something of value received. The codes are identified as a-research or institutional support; b-miscellaneous funding; c-royalties; d-stock options; e-consultant or employee; n-no conflicts disclosed, and *disclosure not available at time of printing.
• The FDA has not cleared this drug and/or medical device for the use described in this presentation (i.e., the drug or medical device is being discussed for an “off label” use). ◆FDA information not available at time of printing. Δ OTA Grant.