OTA 2008 Posters
Scientific Poster #50 Basic Science OTA-2008
Distal Radius Fixation Using Volar Locking Plate Only versus Volar Locking Plate and Synthetic Bone Cement
Utku Kandemir, MD1 (a-AONA, SFGH Foundation);
Amir Matityahu, MD1 (a-Medtronik, Smith + Nephew, Stryker; a,b-AO, Synthes, Zimmer;
a,b,e-DePuy, A Johnson & Johnson Company); Rohan Desai, BS1 (n);
Christian Puttlitz, PhD2 (a-Synthes);
1Department of Orthopaedics, University of California, San Francisco, California, USA;
2Department of Mechanical Engineering, Colorado State University, Fort Collins, Colorado, USA
Introduction: The purpose of this study is to compare fixation of a volar locking plate with and without calcium phosphate bone cement in dorsally angulated and comminuted distal radius fractures (OTA type 23-A3.2).
Methods: Eight matched pairs of fresh-frozen cadaveric forearms were used (mean age 75 years, range 66-88). A 5-mm dorsal gap wedge destabilization model was created 2 cm proximal to the radial articular surface. Paired specimens were stabilized, one side with the volar locking plate only and the contralateral side with volar locking plate and synthetic bone cement (carbonated hydroxyapatite). Cyclic loading was applied to simulate stresses during the postoperative period. Axial and torsional stiffness before and after cyclic loading were measured. Finally, each specimen was loaded to failure in axial compression.
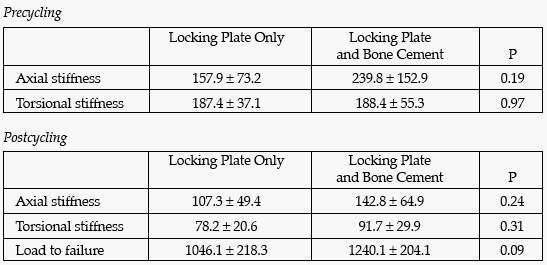
Results: There was no significant difference of bone mineral density between the two groups (P = 0.83). The precycling axial and torsional stiffness of the locking plate only group was not significantly different from the locking plate and bone cement group. Similar results were found after cycling, and there was no significant difference in axial and torsional stiffness. The mean load to failure was greater for the locking plate and bone cement group than the locking plate only group; however, the difference was not significant.

Conclusion: The results of the study demonstrated that fixation with volar locking plate only was as stiff as fixation with a volar locking plate and synthetic bone cement. After cyclic loading simulating applied forces during the healing period, both types of fixation had similar stiffnesses. Load to failure was not significantly different.
Clinical Significance: Intermediate-term fixation obtained with only a volar locking plate is as stable as fixation with a locking plate and synthetic bone cement.
If noted, the author indicates something of value received. The codes are identified as a-research or institutional support; b-miscellaneous funding; c-royalties; d-stock options; e-consultant or employee; n-no conflicts disclosed, and *disclosure not available at time of printing.
• The FDA has not cleared this drug and/or medical device for the use described in this presentation (i.e., the drug or medical device is being discussed for an “off label” use). ◆FDA information not available at time of printing. Δ OTA Grant.