OTA 2008 Posters
Scientific Poster #27 Basic Science OTA-2008
Biomechanical Comparison of a Non-bridging External Fixator and a Volar Plate on a Simulated Comminuted Fracture of the Distal Radius
Elizabeth Anne Ouellette, MD1 (n); Veronica Diaz, MD2 (n); Mohammad A. Hajianpour, MD3
(e-Nutek Orthopaedics); Edward L. Milne4 (a-Nutek Orthopaedics);
David Kaimrajh4 (a-Nutek Orthopaedics); Takashita Sano5 (a-Nutek Orthopaedics);
Loren L. Latta, PhD2, 4 (a-Nutek Orthopaedics, Inc.);
1Miami International Hand Surgery Service, North Miami, Florida, USA;
2University of Miami, Department of Orthopaedics and Rehabilitation, Miami, Florida, USA;
3Nutek Orthopaedics, Inc., Fort Lauderdale, Florida, USA;
4Max Biedermann Institute for Biomechanics, University of Miami, Miami Beach, Florida, USA;
5University of Miami, Department of Biomedical Engineering, Coral Gables, Florida, USA
Background: Comminuted distal radius fractures with five or more bone fragments are difficult to reduce and stabilize with current open reduction and internal fixation techniques because screw placement and purchase is difficult in the small intra-articular fragments of often osteoporotic bone. External fixation can provide stability through ligamentotaxis but immobilization of the wrist joint is required. Nonbridging external (NBX) fixation, which allows for precise, multiplanar pin placement, provides an alternative to volar plate fixation.
Hypothesis: Because of the ability to provide multiplane fixation and accurate pin placement, the NBX fixator should provide better reduction and comparable rigidity of fixation to a volar plate for a five-fragment distal radius fracture.
Methods: Using a biopsy needle, 1.5-mm stainless steel balls were implanted in the distal radius of five fresh pairs of human cadaveric upper limbs to track bone fragments by radiographic images. A simulated five-part distal radius fracture was created. One arm was randomly fixed with the NBX fixator; the matched pair was fixed with a volar plate and screws (VPS). Fluoroscopic images were recorded at the extremes of passive volar-dorsiflexion range of motion (ROM) and radial-ulnar deviation. Finally, each arm was loaded with an axial force at a constant displacement rate until failure.
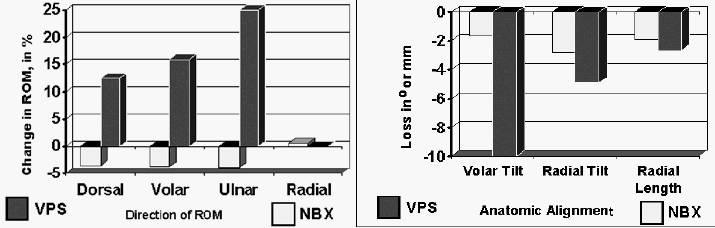
Results: The average loss of radial tilt due to fracture was 16.6° ± 7.2° for the NBX and 11.2° ± 5.5° for VPS. The average loss of radial length was 5.4 ± 4.0 mm for NBX, and 4.6 ± 2.3 mm for VPS. The average loss of volar tilt was 28.0° ± 12.3° for NBX and 24.7° ± 15.7° for VPS. Initial displacement was slightly less for the VPS group, but it was not statistically significant. The average restoration of radial tilt achieved for the NBX group was 13.8° ± 4.8°, and 6.3° ± 4.7° for VPS; radial length was 3.4 ± 3.7 mm for NBX and 1.9 ± 1.0 mm for VPS; and volar tilt was 26.3° ± 12.4° for NBX and 14.0° ± 13.5° for VPS. Only the restoration of radial tilt by NBX was statistically significantly better than VPS. But pairing right versus left arms, the relative restoration of radial length and volar tilt were significantly better for NBX. The ROM was slightly less for the NBX group after fixation compared to ROM before fracture. ROM with volar plating increased after surgery. The peak axial load for NBX was 925 ± 445 N; for VPS, 2152 ± 1023 N. VPS strength was statistically significantly better than NBX.
Conclusion: NBX has minimal effect on ROM and provided adequate restoration of alignment that was at least as good as VPS for this five-part fracture model. Load to failure was more than twice as high for the volar plate.

If noted, the author indicates something of value received. The codes are identified as a-research or institutional support; b-miscellaneous funding; c-royalties; d-stock options; e-consultant or employee; n-no conflicts disclosed, and *disclosure not available at time of printing.
• The FDA has not cleared this drug and/or medical device for the use described in this presentation (i.e., the drug or medical device is being discussed for an “off label” use). ◆FDA information not available at time of printing. Δ OTA Grant.